One of the best ways to learn the English language and improve your English grammar is by learning from mistakes. In this article, we are going to talk about simple and common mistakes students usually make when speaking or writing in English. Let’s start.
These mistakes are made by beginner of lower-intermediate students of English. However, a student of advanced English course should also be aware of such simple mistakes! Let’s begin with the first one:
A basic mistake in talking about your age
1.I am born in Chicago
OK! Here’s a question: When did that happen? Now? In the past? In the future? Most mistakes of English grammar are related to tenses. So, always ask yourself this: When did it happen?
In general, when we want to talk about the place or date of birth, we use simple past. Clearly, it is because it happened in the past, at an exact time and place. That is the definition of simple past!
To talk about the place or date of birth, we use “to be born”. Now, pay attention: you have to choose the correct “to be” verb depending of your subject.
For some subjects, instead of “be born” we should say” was born”.
For example:
- I
- He
- She
We should use “were born” for subjects like:
- You
- We
- They
So, to sum up: instead of saying” I am born in Chicago”; I should say “I was born in Chicago“ or to give the date of birth, I can say “I was born in 1994 “.
2. My sister has 15 years
If you want to talk about your age or someone else’s; you should use this structure:
For example:
- I am 27.
- He is 31
You can also use “years old” at the end. This will make it more formal and more complete.
For example:
- I am 27 years old
- She is 42 years old
Therefore, this sentence is wrong:
- He is 30 years
Instead of that, you should either say
- He is 30
or
- He’s 30 years old
3.Look! it rains
Imagine you open the window and then you see the rain. You tell your friend:
”look! it rains”.
Is that correct? NO!
But why? This sentence is a simple present sentence. The subject is “it” and the verb is “rains”.
To make a simple present sentence, we use this structure:
But when do we use the simple present tense? We use it for general conditions, such as:
- I am a teacher (Generally, that’s my job!)
- I teach English. (As an English teacher, I generally teach the English language!)
So, when we are talking about a situation, a condition or a state in general, we should use present simple. However, if what we are talking about is not in general, and we are talking about what is happening now, we don’t normally use the present simple tense (unless the verb is a non-action verb which is explained later on in this article, so keep reading!). Instead, when talking about something that is taking place now, we use the present continuous tense. Look at these two examples:
- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
- Hey Jack, the water is boiling. Shall I make some tea?
“Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius” and since It’s a fact (and therefore is generally true), we use the present simple to form this sentence. But when something is happening right now, we use the present continuous tense and say “the water is boiling now”.
Present continuous is a tense that we use when we want to talk about something that is happening around now or exactly now.
How to make it?
Now, let’s look back at the wrong sentence:
You look out the window, see the rain and say “look! it rains”.
When does this sentence take place? Is it referring to a general situation, or is it talking about what’s happening right now? Of course it’s happening now, because you are looking outside the window!
Therefore, instead of saying “look! it rains”; you should say “look! it’s raining”.
However, if the sentence is in general, the sentence should be like this: “It often rains here in spring, so remember to take your umbrella!” In this case, it is not raining now, but it generally rains here in the spring!
Now, let’s have a look at common mistakes regarding the present continuous tense.
Learn more: Do you know the phrases and vocabulary about English newspaper? Follow the link below to get familiar with them!
English newspaper vocabulary
4.It is often raining
I think now you can tell why this sentence is wrong!
This sentence is in the present continuous tense which can also be called present progressive. The sentence is composed of a subject (it), to be verb (is), and a main verb with -ing (raining). Moreover, we have an adverb of frequency which is “often”. Wrong use of adverbs of frequency in present progressive sentences is one of the most common mistakes among students! So first, let’s have a look at adverbs of frequency in English.
What is an adverb of frequency?
An adverb of frequency shows how often something happens. For example:
| Always | when something happens all the time |
| Usually and often | when something happens 80% percent of the time |
| Sometimes | when something happens around 50% percent of the time |
| Seldom, hardly ever, and rarely | when something happens less than 50% of the time |
| Never | When something never happens and has zero percent chance of happening |
In the example above, we used “often “ which means it happens 80% of the time. As discussed earlier. when we are speaking about something in general and not right now, we use the simple present tense.
So instead of saying “It is often raining here”; you should say “It often rains here”.
Note that the adverb of frequency comes directly before the main verb.
When you just started to study grammar, you may think that simple tenses are simple just like their names, but when you actually want to use them, sometimes they become very confusing. So be careful!
5. I am not believing him
Imagine I am talking to a friend of mine right now, and he tells me that there are no buses in China.
Because this conversation is happening right now, I should use the present progressive tense and say that “I’m not believing him”.
It sounds logical, right? But there is something wrong here.
Not all verbs accept -ing. We can only use “ing” with action verbs.
What is an action verb?
An action verb is a verb that includes a sort of action (or a physical activity) that you need to spend energy on. Like:
- Walking (you move your legs and feet to walk)
- Talking (you move your mouth and tongue to talk)
- Sleeping (You close your eyes, lie down and sleep)
- Sitting (you put your bottom on a chair!)
- Standing (you use your legs to stand)
All these activities require energy.
However, some verbs are called stative verbs (or non-action verbs). These verbs either describe things or talk about mental (and not physical) states. For example:
- I believe in god (Do I need energy to believe in god? No! believing is a mental state)
- I like chocolate (Do I burn any calories just because I like chocolate?! I don’t need energy to like chocolate!)
Non-action verbs DON’T take “ing”. Therefore, the initial sentence “I’m not believing him” is wrong, since “believe” is a non-action verbs and does not accept -ing.
What should I use instead? Even though the action is taking place right now, since the verb is non-action, we use simple present:
“I don’t believe him”
OK, enough with the present tense! Let’s talk about the past.
Learn more: What is the vocabulary about food in English?
6.When I was 20, I was smoking
At the age of 20, I smoked. It was a habit and I was addicted to smoking. The tense of the sentence “I was smoking” is past continuous. We use the past continuous to talk about something that happened once and lasted for a while.
For example:
- Yesterday between 2 and 4 p.m. I was studying (I am talking only about yesterday afternoon, and the action lasted for 2 hours)
But at the age of 20, I smoked all the time. It was something that happened regularly and was repetitive. For repeated actions in the past, we use simple past and not past progressive. Therefore, we should say
- When I was 20, I smoked
To make it clear, look at these two examples:
- As a child, my brother played tennis every day (the action “play tennis” was a repeated action in the past, Therefore, we use past simple)
- Sorry I rejected your call. I was playing tennis. (When you called, I was in the middle of an action that lasted for a while and was not repetitive)
That was about simple past and past continuous. However, even more confusing than this is the difference between simple past and present perfect!
The confusion between “Simple past” & “Present perfect”
We use simple past to talk about something that happened in the past and is over now. On the other hand, present perfect also refers to something that happened in the past, but whose effect is still present! Confusing? Let me clarify:
To make a simple past sentence, we use this structure:
To make a present perfect sentence, we use this structure:
Now, look at this sentence.
Learn more: Read the article about the formal and informal English words
7.I have seen Jack yesterday
For the past events, we can use both present perfect and simple past. But what’s the difference?
If you are talking about a very specific moment, people, or place in the past, you should use the simple past tense.
In the example above, since the time of the sentence is specific (yesterday), we should say: “I saw jack yesterday”.
When do we use present perfect?
Imagine you are going out with a friend (Jessie) and then you see another person (Jack) who is a friend of your friend.
In this example, Jesse who’s a friend of you and Jack, wants to introduce you and Jack to each other.
But you saw Jack yesterday and you know him. So you would tell her “I’ve seen jack before”
You are not referring to the exact moment when you saw Jack. The important thing is that you know Jack.
If Jesse asks “when did you see Jack?” you would say ”I saw Jack yesterday at the party”!
for modal verbs
8. I can to swim / I must to study hard
Can and must are modal verbs.
What are modal verbs?
Can, could, should, would, may, might, must and some other verbs are called modal verbs.
After modal verbs, we do not use the infinitive with to. Instead, we use “bare infinitive” which is basically an infinitive WITHOUT “to”. Therefore, we should say:
- I can swim
- I must study hard
Remember: After modal verbs, we must always use the simple form of the verb. We cannot use:
| Wrong | Correct |
| -ing form: I must going home | I must go home |
| Past form: I must ate lunch | I must have eaten lunch (past form of modal verbs: Modal + Have + Past Participle of the verb) |
| Future: I must will travel abroad | I must travel abroad (must and will are both modal verbs, and we cannot have 2 modal verbs at the same time) |
double negatives
9. I looked but I didn’t see nothing
Look at this sentence: I ate something for lunch. How do you make it negative? There are 2 ways:
- I didn’t eat anything.
- I ate nothing.
We use “didn’t” to make a negative simple past sentence. If you don’t want to use “didn’t”, you can use “nothing” instead of “anything”. So both of the above-mentioned sentences are negative.
Attention: You can only have ONE negative in a sentence, and not 2!
Therefore, the sentence “I looked but I didn’t see nothing” has 2 negatives, and therefore it’s wrong. But what is the correct form? There are 2 correct forms:
- I looked, but I didn’t see anything.
- I looked, but I saw nothing.
Talking about the purpose of an action: To or For
10. I came here for study English
The reason why I came here was to study English. That is my purpose. Whenever you want to talk about your purpose; you use “to” and NOT “for”.
Whenever you want to talk about your purpose; you use “to” and not “for”.
For example:
- I sat down to rest
Why did you sit down? I was tired and wanted to rest. So that is the purpose. Here’s another example:
- He went abroad to study
- I’m going to Australia to learn English
Watch this video about 5 common grammar mistakes
yes/no questions and WH questions
11. Is ready my new office?
This sentence is completely wrong. To understand this mistake, pay attention to this affirmative sentence:
- My new office is ready.
To make a yes/no question, you put the auxiliary verb in the beginning. In this sentence our auxiliary verb is “is”. So, let’s put it first:
- Is my new office ready?
Instead of saying “is ready my new office” you should say “is my new office ready?”.
12. Where I can buy stamps?
This sentence isn’t correct. For a better understanding, look at this positive sentence.
- I can buy stamps.
It’s a positive simple present sentence. If I want to make a yes/no question out of this positive sentence, I simply take the auxiliary verb and put it in the beginning.
An auxiliary verb is a verb that is not the main verb of a sentence. “buy” is the main verb and “can” is a modal verb. Since “can” is not the main verb, it’s the auxiliary verb. To make a yes/ no question, we should put “can” at the beginning of the sentence.
To make a yes/no question: Take the auxiliary verb and put it in the beginning.
like this:
- Can I buy stamps?
You can also make this sentence with “wh question word”.
What is a “wh question word”?

To make a “Wh question”, put a Wh- question word at the beginning of a yes/no question! Look at these examples:
- Why can I buy stamps?
- When can I buy stamps?
- Where can I buy stamps?
Therefore, instead of saying” where I can buy stamps?” which is wrong, you should say “where can I buy stamps?”.
In general, to make a full question, you can use this structure:
For example:
- Where do you come from?
- Why does she work here?
- When do they have a meeting?
Learn more: tools to practice english
So, try to avoid these simple mistakes in question formation! Now, let’s have a look at another very common mistake:
Subject-verb agreement
13. Everybody were tired
This is a very common yet simple mistake. What’s wrong with it?
In this sentence, “everybody” means “a group of people” or “all people” and “were” is the past of “are”.
It means they were tired back then. “We’re tired” sounds right but” everybody were tired” is completely wrong and the reason is that in the English language, we use singular verbs for these pronouns:
| Everyone | + Singular verb |
| Everybody | + Singular verb |
| No one | + Singular verb |
| Nobody | + Singular verb |
| Someone | + Singular verb |
| Somebody | + Singular verb |
Therefore, we must say:
- Everybody is tired
- Nobody is ready
- Somebody is sad
If we are talking about the past, we should clearly use “was” instead of “is”:
“Everybody was tired”.
adverb placement
14. I like very much skiing
This sentence is completely wrong. But what’s wrong with it?
“Very much” is an adverb here and the place of adverb is not correct.
Where do adverbs go?
We use adverbs to describe a verb. Adverbs of manner go either after the verb or if the verb has an object, it goes after the verb phrase.
What is a verb phrase?
In our example, “like” is the verb and “skiing” is the object. According to the definition above, ”like skiing” is the verb phrase. Adverbs should go after the verb phrase. We have to say “I like skiing very much” instead of saying “I like very much skiing”
Where to put “enough”
15.The soup isn’t enough hot
This simple mistake is a very common in English and among students. The position of “enough” is not correct here.
What is the correct position for “enough”?
“Enough” should go before nouns. For example:
- Enough money
- Enough food
- Enough chairs
- Enough space
“Enough” can also go after an adjective or verb. Such as these sentences:
- Hot enough
- Cold enough
- High enough
- Good enough
- Strong enough
- Work enough
- Exercise enough
- Study enough
Look at this sentence again:
- The soup isn’t enough hot
“Hot” is an adjective and “enough” should be after the adjective. Therefore, you should say “the soup isn’t hot enough”.
Learn more: The most common boring words in English and their alternatives
collocations and structures
16. I gave to her my address
When you want to use “give” in a sentence; you should use one of these two structures:
For example:
- Give me the chair / Give the chair to me.
- Give me your number / Give your number to me.
- Give her the card /Give the card to her.
We never use “to” after the verb “give”.
17. I did a mistake
We make a mistake. If you want to use “mistake” in a sentence, the verb that collocates with it is “make”, NOT “do”.
The word “Mistake” collocates with “make”.
Look at these examples:
- I made a mistake.
- I made a terrible mistake.
- I made a bad mistake.
- I made a horrible mistake.
- My father made a terrible mistake.
So, be careful not to make mistakes with English collocations! A very good tool to look up collocations is OZDIC. It’s a collocation dictionary. Give it a try!
18.We went at the seaside on Sunday
What’s wrong with this sentence? “Went” is the past tense of “go” and after go, we should use the preposition “to”. Like:
- Go to a place.
- Go to the beach.
- Go to the seaside.
- Go to a supermarket.
- Go to work.
- Go to school.
Exception!!!
If you want to put “home” after “go”, you don’t need to use “to”.
- Go home.
So, the correct form of the sentence is: “we went to the seaside on Sunday.”
singular/plural nouns mistakes
19. The people in this town is very friendly
This sentence isn’t correct because “people” is the plural form of “person”. Instead of “the people is” you should say “the people are”. We use “are” For “children” and “mice” as well because they are the plural form of “child” and “mouse”.
Therefore, you should say “the people in this town are very friendly”.
20. The news were shocking
This sentence isn’t correct, because “news” is not plural. Although the word “S” is placed at the end of the word “news”; But it does not mean that the word is plural.
Eventually, the sentence should be like this:
“The news was shocking” or “the news is shocking”.
Learn more: If you are into news, follow the link below to learn about English newspaper vocabulary:
English newspaper vocabulary
21. What did you do at 8 o’clock yesterday evening?
What do you think is wrong with this sentence?
We use the simple past to talk about an action at or about a specific time in the past. But when we want to talk about something which was happening around a particular time in the past, we use past continuous.
The tense of the question is simple past. (What did you do?) but since we are talking about a specific time in the past (8 o’clock), we should use past continuous. Therefore, the correct sentence is like this:
- What were you doing at 8 o’clock yesterday evening?
Learn more: how to talk about time in english
22. When I was a child, we were walking to school every day
How many times did this action happen? Was that only once? No!
It was a repeated action in the past and when we want to talk about a repeated action in the past, we use simple past tense.
So, the correct sentence would be like this:
- When I was a child, we walked to school every day.
Here is another example:
- As a kid, we played volleyball every evening. (playing volleyball was a repeated action in the past.
23. Some people think that Shakespeare has traveled in Germany
What do you think is the tense of this sentence? It’s in the present perfect tense, right?
We use present perfect to talk about something which happened in the past with a connection to the present. As an example:
- I have broken my leg! (It happened in the past but I can see the effect right now and my leg is still broken)
Have a look at this sentence:
- I broke my leg!
This sentence is in past simple tense and it means that my leg is not broken anymore. So, we use the simple past to talk about something which happened in the past and finished.
To recap:
- I have broken my leg! à you did it in the past, but your leg is still broken.
- I broke my leg à you did it in the past but your leg is not broken anymore!
Let’s get back to the original sentence. Is there any connection between Shakespeare’s traveling to Germany and the present time? No! because there is no Shakespeare right now (R.I.P). So, there is no connection to the present time and the action is finished and we should use simple past:
- Some people think that Shakespeare traveled in Germany.
Learn more: traveling phrasal verbs
24. When has the accident happened?
What is the tense of this question? Present perfect.
Remember that when we want to talk about a specific time in the past (ex: last year, last month, etc.) we use simple past. For example:
- Yesterday I had an accident!
Similarly, when we are asking about when something happened in the past, we use past simple (again!).
So, in the sentence above, we are sure that the accident happened in the past and we want to ask about the time, therefore we need to use simple past:
- When did the accident happen?
25. This is the first time I hear her sing
What’s wrong with this sentence?
This sentence is in simple present. However, with structures such as
- This is the first time….
- This is the third movie……
- This is the fifth day….
We use present perfect. For example:
- This is the third movie I have seen this week.
- This is the third time you have called me today.
And the correct form of the sentence would be like this:
- This is the first time I have heard her sing.
A challenge for you!!
Look at this sentence:
- I told her that I have finished.
What’s wrong with this sentence? You can write your answer in the comment section of my YouTube channel. Just click here!
Learn more: personality adjectives
26. How many languages did you bring with yourself?
What’s wrong with this sentence?
The problem is with the word “luggage”. Luggage means anything we take with ourselves when we travel. But pay attention that this word is not countable. So, since it’s an uncountable noun, you cannot say “luggages”.
If you want to address more than 1 luggage, you can use “pieces of”:
What’s wrong with this sentence?
The problem is with the word “luggage”. Luggage means anything we take with ourselves when we travel. But pay attention that this word is not countable. So, since it’s an uncountable noun, you cannot say “luggages”.
If you want to address more than 1 luggage, you can use “pieces of”:
- A piece of luggage
- One piece of luggage
- Two pieces of luggage
Another thing you can do is to replace “luggage” with “suitcase”. Then you can say “I have two suitcases”.
27. Latest researches have given us a better life
What’s wrong with this sentence?
The problem is with the words “research”. This word as a noun is uncountable and if we want to fix the problem we need to change “have” to “has” because “research” is singular. So, the correct form of the sentence would be like this:
- Latest research has given us a better life.
28. That gym is really expensive because of all its modern equipments
The problem with this sentence is with the word “equipments”. Equipments is not countable. To correct the sentence we should say:
- That gym is really expensive because of all its modern equipment.
Alternatively, instead of equipments you can say “amenities”. Amenities mean facilities and it’s countable.
Learn more: sports phrasal verbs
29. The news this morning were terrible. Prices are increasing again
What’s wrong with this sentence?
The mistake is about the word “news”. Pay attention that even though “news” has an “s”, it’s not plural and it’s singular. So, we need to change the verb to “was”. The correct form of the sentence will be like this:
- The news this morning was terrible. Prices are increasing again.
If you want to talk about just one particular news, you should say:
- A piece of news (it’s not very common though).
- A news item / news items (All the news items were sad this morning.)
30. I live on the outskirt of the city
“Outskirt” should be “outskirts”. But why?
Outskirts mean the outer part of a town or a city. “Outskirts” is a plural noun and it doesn’t have a singular form.
The correct preposition for this word is “on”. So, in the “outskirts” or “at the outskirts” is wrong.
31. The fishmonger weighed out 3 kilograms of fishes
What’s wrong with this sentence?
“Fish” is uncountable and you can’t say 3 kilograms of fishes. Look at these examples:
- I saw three fish in the tank.
- I ate one kilogram of fish.
- My mom cooked five kilograms of fish.
The correct form of the sentence would be like this:
- The fishmonger weighed out 3 kilograms of fish.
*But, “fish” has an irregular plural. This means that we only use “fishes” when we are talking about different types or different species of fish.
- We have three fish in our tank. (we have three fish of the same kind).
- We have three fishes in our tank. (we have three different species of fishes in our tank.)
Learn more: idioms related to cat
32. The sceneries in Switzerland are beautiful
“Scenery” means what you can see in a natural environment. However, this word is not countable. Remember that you change the verb from “are” to “is”.
- The scenery in Switzerland is beautiful.
33. The police is aware of the crime
The problem is with the word “is” because “the police” is a plural noun and you should use a plural verb with it. the correct form of the sentence will be like this:
- The police are aware of the crime.
But if you are talking about people who are members of the police and you want to address one of them, you should either use cops (countable noun) or police officers (countable noun). You can also say a policeman or a policewoman. But pay attention that the plural form is policemen and policewomen.
34. My uncle is a professor of economic
“Economic” is an adjective and it needs a noun (ex: economic decisions of the factory, economic climate of the country). What you teach / learn at university is economics. Economics is the science of economy and this word is always plural.
- My uncle is a professor of economics.
35. We need to gather new informations about the subject
What’s wrong with this sentence?
The word “information” is not countable. But what if I want to talk about one information? In that case, I should say “a piece of information”.
- We received a valuable piece of information and it can help us a lot.
The correct form of the sentence will be like this:
- We need to gather new information about the subject.
To learn more about these examples watch the following video on Youtube!
Is this scenario familiar to you?
You’ve studied hard for your exam and you confidently took it and you are so sure about the results. But when the results come, instead of nailing it, you have ruined it! Especially in the section, you were confident about the most! (Aka grammar).
So stay with us to learn more about common grammatical mistakes in English
36. Could I have some butter and bread?
What do you think is the problem with this sentence?
In English, some word pairs are fixed and you have to respect the order. For example salt and pepper. We always say them in this order and nobody says pepper and salt.
These are called binomial pairs which means a pair of words that are always fixed. Let’s have a look at some other examples:
- Bread and butter
- Knife and fork
- Cup and saucer
- Black and white
- Thunder and lightning
You will always have to respect the order. But if you use the opposite order, people will still understand you and it’s not wrong but it sounds weird.
So the correct form of the sentence would be like this:
- Could I have some bread and butter?
37. He doesn’t smoke and drink
Can you detect the mistake?
Have a look at the verb. Is it positive or negative?
When you have a negative verb and you want to talk about 2 things, you should use “or”. For example:
- We weren’t comfortable or happy.
When you have a positive verb and you want to talk about 2 things, you should use “and”. For example:
- We were comfortable and happy.
So since the verb of the sentence is negative, the correct form will be like this:
- He doesn’t smoke or drink.
38. The project wasn’t successful in economic terms and in political terms
This one is easy. Similar to the previous one, the verb of the sentence is negative. So, instead of “and” you should use “or”.
The project wasn’t successful in economic terms or in political terms
One use of conjunction such as or / and is to avoid repetition and make simpler and more clear sentence structures. So, instead of repeating “in” and “terms” twice, we can make the sentence shorter in this way:
- The project wasn’t successful in economic or political terms.
Learn more: how to improve english vocabulary
39. Both he can borrow the bike and he can use the car
Let’s dig into “both”:
We use it in balanced structures (Both……and…..). balanced structures can be in different forms:
Both noun and noun
- I spoke to both the director and the secretary.
Both verb and verb
- She both dances and sings.
Both adjective and adjective
- She is both pretty and clever.
Both can be used in unbalanced structures as well. They are not wrong but not very common. For example:
- She both dances and she sings. (Both verb and clause)
But remember that you cannot use both before a clause! This sentence is wrong:
In the main sentence, both came before a full clause and that’s why the sentence is wrong. The correct form of the sentence will be like this:
- He can both borrow the bike and use the car.
40. Although she was tired, but she went to work!
In this sentence, you can see “but” and “although”. “But” and “although” are conjunctions which means they link two sentences together!
The point is that you should only use one of them in a sentence and not both of them together. So the correct form of this sentence is one of these:
- She was tired, but she went to work
- Although she was tired, she went to work.
A challenge for you!!
Look at this sentence:
- Because I liked him, so I tried to help him!
Try to answer these questions:
- what is wrong with this sentence?
- what is the correct form of this sentence?
You can click here and submit your answers in the comment section of the video.
Let’s learn 5 other simple grammar mistakes!
41. I laid down and went to sleep
What is wrong with this sentence?
The problem is with the verb “laid”.
There are 2 very confusing and similar verbs in the English language
- To lay
To lay means to put something down or to put something somewhere. For example:
- I’m going to lay the notebook on the table.
- If the baby falls asleep, you should lay him down.
- To lie
To lie means to go in a horizontal position. For example:
- I would lie in bed.
- I’m so tired. I want to lie down on the couch.
Everything seems crystal clear right now. But the problem begins when we want to talk about the past.
Now let’s go back to the original sentence:
- I laid down and went to bed.
In this sentence, we are talking about the past. Right? So, we should use the past form of “lie” which is “lay”.
- I lay down and went to bed.
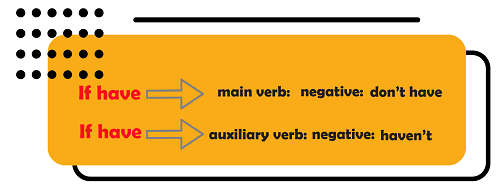
42.I haven’t a car, I travel by train
Can you spot the problem? Yes, the problem is with “haven’t”.
Look at these three sentences:
- I have a car.
- I have a meeting.
- He has cereal for breakfast.
The main verb for all these sentences is “have”.
Now let’s make them negative:
- I don’t have a car.
- I don’t have a meeting.
- He doesn’t have cereal for breakfast.
So, when we want to make negative sentences with the verb “have”, we use “don’t have” not “haven’t”. This is true for the simple present. However, if you want to use present perfect, things are different. Look at this sentence:
- I have played tennis.
In this sentence, “played” is the main verb, and “have” is the auxiliary verb. When “have” is an auxiliary verb (usually in present prefect), instead of “don’t have” you should use “haven’t” to make the sentence negative.
- I haven’t played tennis.
So to sum up
Therefore, the correct form of the sentence would be like this:
- I don’t have a car, I travel by train.
Learn more: problem solution phrasal verbs
43. Can you suggest me a good dentist?
The problem in this sentence is with the use of the word “suggest”. But how can we use it correctly?
There are 3 different ways to use “suggest” correctly:
We use this structure when we want to talk about activities.
So, let’s go back to the original sentence:
- Can you suggest me a good dentist?
As you’ve seen above, you should suggest something to somebody. Therefore, the correct form of the sentence will be like this:
- Can you suggest a good dentist to me?
44. Please describe me your father
What’s wrong?
That’s right! There is a problem with the use of the verb “describe”.
Just like “suggest”, you can use “describe” in this form:
So, instead of saying “describe me your father”, you should say:
- Describe your father to me.
Let’s see some more examples:
- Can you describe your best friend to me?
- Could you describe your hometown to me?
- Can you describe your parents to me?
- I can’t remember her, can you describe her to me?
These sentences are wrong:
- Describe me your parents.
- Describe me your father.
45. It is a lot of noise in the street!
There is a problem with the use of the pronoun “it” in this sentence.
When you want to say that something exists somewhere, you don’t use “it”. In these cases, you should use “there”. For example:
- In my bedroom, there is a phone. (I’m talking about its existence.)
- Here, there is a microphone.
- There is an iPad on my desk.
- There is a power bank.
If the things you are talking about, are more than one, you should use “there are” instead of “there is”. For instance:
- There are some books on my desk.
If you are talking about the past, you can use “there was / were”. For example:
- There was a tall guy at the party yesterday.
- There were many beautiful girls at the party yesterday.
So, the correct form of our sentence should be like this:
- There is a lot of noise in the street.
The reason why we use “there is” instead of “there are” is that “noise” is singular.
Watch this video about the last 5 grammar mistakes mentioned in this article.
Conclusion
In this article, we talked about simple mistakes in English that student often make, especially in writing and speaking. So read this article again to improve your speaking , grammar, vocabulary and writing skills. You can also join my English courses where I teach you grammar and vocabulary as well as the 4 skills of Speaking, Reading, Writing and Listening.(Go to the menu bar on my website and click on the courses!)
Here is the brief conclusion of the usage of tenses mentioned in this article.
| Tense | Usage |
| Present simple | To talk about general situations and facts |
| Present continuous | To talk about something that is happening around now or exactly now |
| Past simple | To talk about something that happened at a very specific moment in the past and finished |
| Past continuous | To talk about something that happened once and lasted for a while |
| Present perfect | To talk about experiences, or something which happened in the past and we can still see the result in the present |
Here is the summary of the countable and uncountable words mentioned in this article:
✅Luggage is not countable
- A piece of luggage
- Suitcase / suitcases
✅ Research is uncountable
✅ Equipment is uncountable
- Amenity / amenities
- Facility / facilities
✅ News is a singular noun
✅ Outskirts is a plural noun
✅ Fish is uncountable unless you are talking about different types of fish.
✅ Scenery is uncountable
✅ The police is a plural noun
- Police officer / police officers
- Cop / cops
- Policeman / policemen
- Policewomen / policewomen
✅ Economics is the science of economy and always plural
✅ Information is uncountable
- A piece of information / two pieces of information
I hope you have enjoyed this article!
Remember: one of the best ways of learning English grammar is to learn from mistakes!



































Hello..I really like your all the videos. I would like to study from pdf as well. So can u please send me all the pdf please.
Thanks very much my name is Maxime I really enjoyed with the course so I would like to ask you to give me all courses you have been made in order to improve my English
Thanks again
Can you please send me the pdf of commonly mistaken sentences?.
I want to learn more
Very good thniks